Temperature

In response to increasing greenhouse gas (GHG) concentrations, air temperature over Burkina Faso is projected to rise by 1.9 to 4.2 °C (very likely range) by 2080 relative to the year 1876, depending on the future GHG emissions scenario (Figure 2). Compared to pre-industrial levels, median climate model temperature increases over Burkina Faso amount to approximately 2.0 °C in 2030, 2.3 °C in 2050 and 2.4 °C in 2080 under the low emissions scenario RCP2.6. Under the medium / high emissions scenario RCP6.0, median climate model temperature increases amount to 2.0 °C in 2030, 2.6 °C in 2050 and 3.6 °C in 2080.
Very hot days
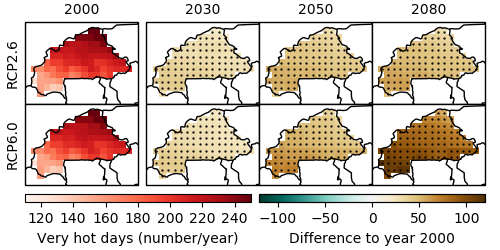
In line with rising mean annual temperatures, the annual number of very hot days (days with daily maximum temperature above 35 °C) is projected to rise dramatically and with high certainty all over Burkina Faso (Figure 3). Under the medium / high emissions scenario RCP6.0, the multi-model median, averaged over the whole country, projects 32 more very hot days per year in 2030 than in 2000, 52 more in 2050 and 88 more in 2080. In some parts, especially in south-western Burkina Faso, this amounts to about 250 days per year by 2080.
Precipitation

Future projections of precipitation are less certain than projections of temperature change due to high natural year-to-year variability (Figure 4). Out of the four climate models underlying this analysis, two models project a decreasing trend in mean annual precipitation over Burkina Faso, while the other two models project an increase. Median model projections show strong interannual variability but no clear trend in mean annual precipitation until 2080 under either RCP.
Heavy precipitation events

In response to global warming, heavy precipitation events are expected to become more intense in many parts of the world due to the increased water vapour holding capacity of a warmer atmosphere. At the same time, the number of days with heavy precipitation events is expected to increase. However, this tendency can only be found in half of the climate projections for Burkina Faso. Median climate model projections show no change in the number of days with heavy precipitation under either RCP (Figure 5). The year 2080 is projected to receive 8 days of heavy precipitation, which is equal to the year 2000.
Soil moisture

Soil moisture is an important indicator for drought conditions. In addition to soil parameters and management, it depends on both precipitation and evapotranspiration and therefore also on temperature, as higher temperatures translate to higher potential evapotranspiration. Annual mean top 1-m soil moisture projections for Burkina Faso show a decrease of 2.5 % for both RCP2.6 and RCP6.0 by 2080 compared to the year 2000 (Figure 6). However, there is considerable modelling uncertainty as different hydrological models project different directions of change, which makes it difficult to identify a clear trend.
Potential evapotranspiration

Potential evapotranspiration is the amount of water that would be evaporated and transpired if sufficient water was available at and below the land surface. Since warmer air can hold more water vapour, it is expected that global warming will increase potential evapotranspiration in most regions of the world. In line with this expectation, hydrological projections for Burkina Faso indicate a stronger rise of potential evapotranspiration under RCP6.0 than under RCP2.6 (Figure 7). Under RCP6.0, potential evapotranspiration is projected to increase by 2.7 % in 2030, 3.8 % in 2050 and 6.8 % in 2080 compared to year 2000 levels.
4 Changes are expressed relative to year 1876 temperature levels using the multi-model median temperature change from 1876 to 2000 as a proxy for the observed historical warming over that time period.



